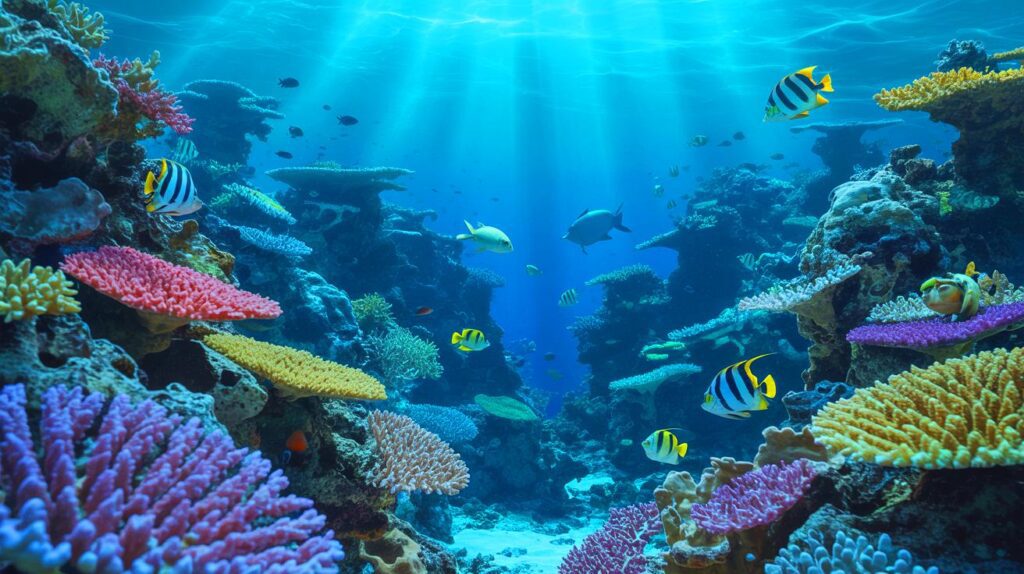
The 2023 ocean heat wave has profoundly impacted 96% of the world’s oceans, breaking records in both intensity and duration. This phenomenon has led to widespread coral bleaching, threatening marine biodiversity and disrupting ecosystems. The heat waves, which were four times longer than historical norms, affected key regions like the North Atlantic and Tropical Pacific.
The causes include a mix of natural factors, like changes in ocean circulation and increased solar radiation, combined with human-induced climate change, such as greenhouse gas emissions. These elements have intensified the absorption of heat in oceans, worsening existing challenges for marine life.
The repercussions are significant: coral reefs are dying, disrupting vital habitats for marine species, and fisheries face massive economic losses, which could total billions of dollars. The ongoing rise in ocean temperatures also correlates with broader climate instability, including polar ice melting and more severe weather patterns.
This situation highlights the urgent need for adaptive strategies to mitigate these changes and safeguard both marine ecosystems and communities reliant on them.
Source link