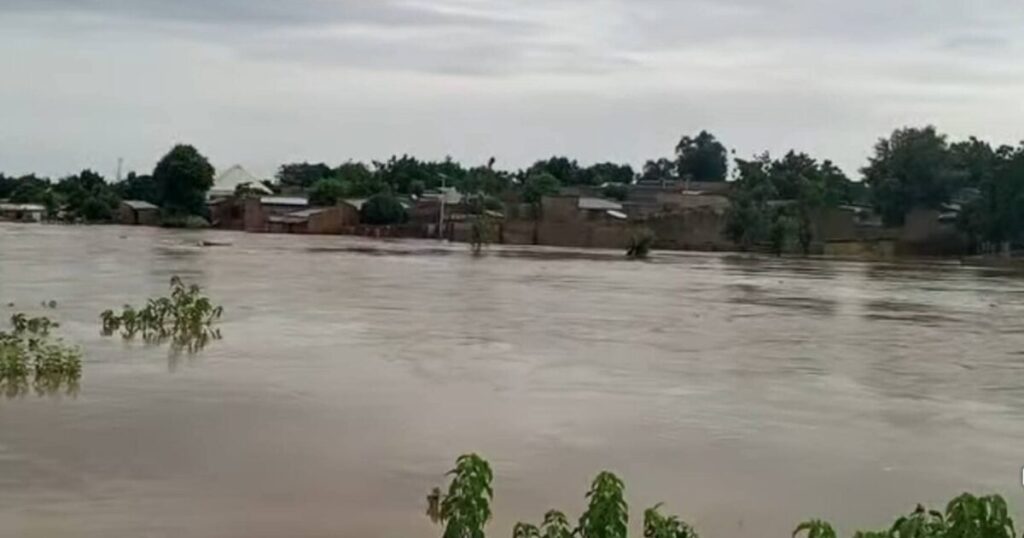
Between January and August 2025, extreme weather conditions led to thousands of deaths and widespread destruction, primarily due to climate change. This highlights the urgent need for coordinated global action to address escalating threats from weather-related disasters.
Significant events included catastrophic floods in northern Nigeria, particularly a deadly flood in Mokwa on May 29 that resulted in over 200 fatalities and hundreds missing. While flooding has occurred in past years, the scale this year was unprecedented, exacerbated by deforestation. Additionally, a heat wave in Europe caused over 2,000 deaths, and a landslide in Sudan’s Mara Mountains killed around 370 people due to heavy rain.
In Gurugram, India, heavy rainfall trapped thousands of commuters for hours, while in Yemen, floods affected over 100,000 people, damaging infrastructure and threatening agricultural production amidst ongoing civil strife.
Further disasters included a magnitude 5.2 aftershock in eastern Afghanistan, following a previous quake that killed over 1,400. Flash floods also occurred in San Antonio, Texas. Climate change is linked to an increase in severe storms and flooding globally.
The Paris Agreement, adopted in 2015, aims to limit global warming and requires countries to commit to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Proposed solutions include transitioning to renewable energy, enhancing early warning systems, and promoting sustainable practices. In Nigeria, integrating warnings from meteorological services and actively addressing deforestation and land misuse are vital steps for resilience against extreme weather events.
Source link