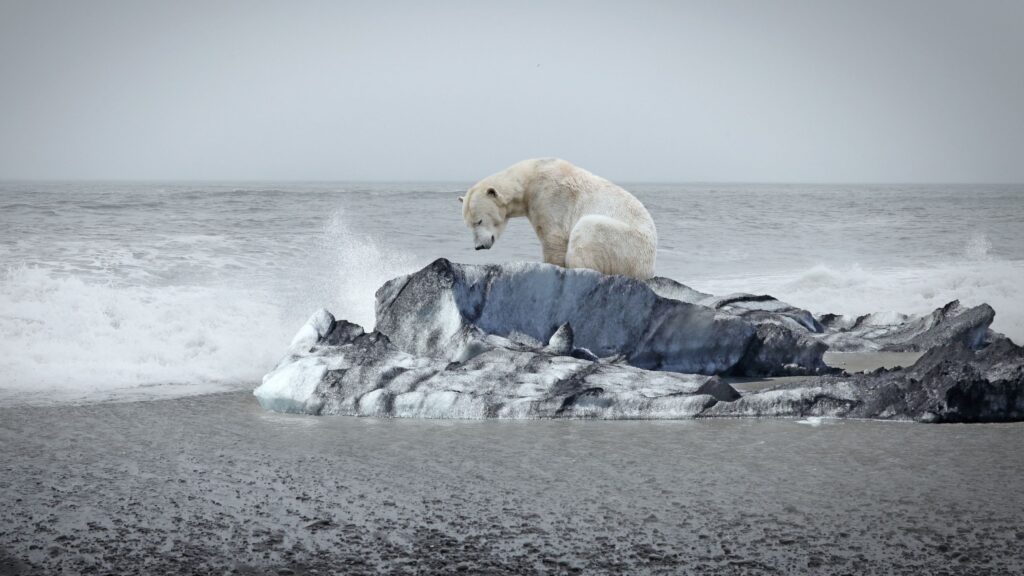
Climate scientists warn that global warming could lead to “tipping points,” irreversible thresholds within Earth’s systems that trigger permanent environmental changes. Major tipping points include the collapse of polar ice sheets, thawing permafrost, and widespread forest dieback. Once a tipping point is crossed, it can initiate feedback loops, accelerating climate change and potentially sending the Earth into a fundamentally altered state, posing severe risks to both nature and humanity.
Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, release greenhouse gases like CO2 and methane, increasing global temperatures. This warming can disrupt natural processes that absorb these gases, further amplifying the problem.
A significant concern is the thawing of Arctic permafrost, which releases trapped carbon into the atmosphere, exacerbating warming. Similarly, ice sheets in Greenland and West Antarctica are nearing tipping points, risking significant sea-level rise. Current climate agreements may be insufficient to prevent these critical thresholds from being crossed.
Deforestation in the Amazon exacerbates climate issues, pushing the rainforest toward a tipping point that could transform it into a savannah. While the situation is complex and fraught with uncertainties, the path to mitigating climate change is straightforward: reducing carbon emissions is essential to avoid crossing dangerous tipping points. Experts emphasize the urgency of immediate action to limit damage and mitigate risks.
Source link