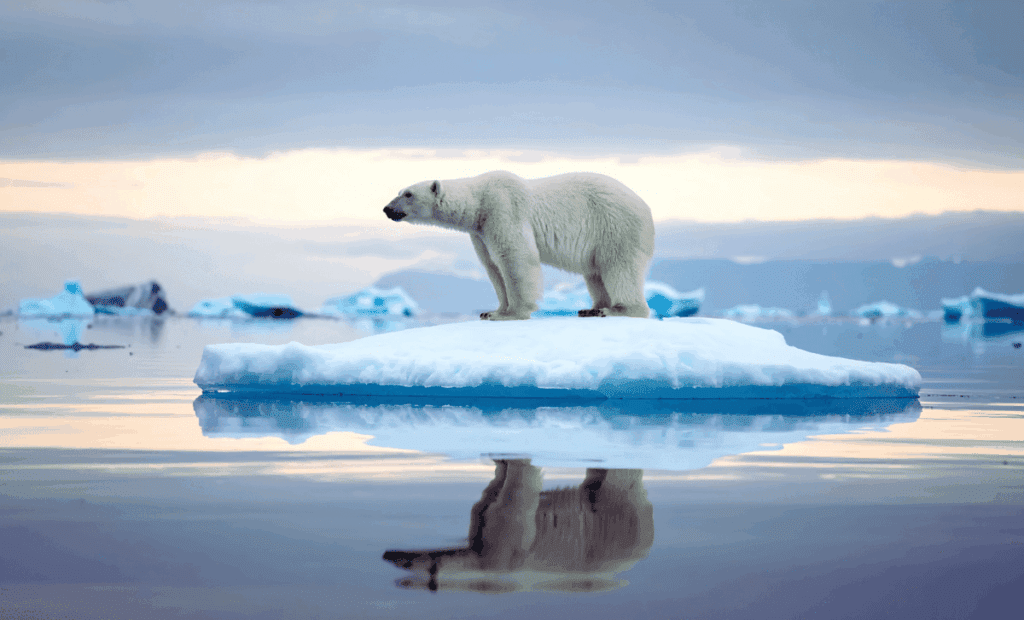
Scientists warn that the Arctic is entering an unpredictable phase of extreme weather due to rapidly rising temperatures, which are increasing more quickly than in other regions. A study published in Science Advances highlights the growing frequency of intense weather events, such as heat waves and rain-on-snow, which pose threats to both wildlife and human populations.
Key findings include:
-
Increased Frequency of Extreme Events: The Arctic is experiencing more extreme weather occurrences, many of which have arisen in areas previously unaffected. This includes heat waves and potentially dangerous rain-on-snow events.
-
Disruption of Seasonal Patterns: Seasonal cycles crucial for the survival of Arctic species are being disrupted. Changes in snow and ice conditions, like the formation of ice layers from rain on snow, hinder access to food for herbivores such as reindeer, which depend on stable conditions.
-
Impact on Global Climate: The Arctic’s changes are significant for the Earth’s climate system. The loss of sea ice affects heat retention and global warming due to darker ocean surfaces absorbing more heat, creating a feedback loop.
- Carbon Release: Thawing permafrost releases stored carbon, further accelerating climate change. This “carbon feedback loop” is crucial in understanding Arctic impacts on global warming.
The study underscores the urgency of addressing these changes before reaching critical thresholds, emphasizing that Arctic climate change is a global issue with widespread implications.